EBA suggests that the number of regulations will not be reduced. At the same time, the mission of the EBA is to create uniform regulatory and supervisory principles for the entire banking sector in all the European Union member states. While the directives are transposed in such a way that sometimes we can see clear differences in interpretation, the technical standards contained in the delegated regulations are the same for all EU countries. This is also the objective of the Single Rulebook, which is a uniform set of rules for the banking sector that is to apply throughout the European Union.
The EBA also wants to promote the convergence of supervisory practices and activities concerning the resolution of the banks. This mainly involves the consistent application and consistent enforcement of the provisions in all countries in the same manner. But it is also a platform where representatives of supervisory authorities from all the member states, gathered at colleges of supervisors, hold discussions concerning the effective implementation of regulations and standards, and the assessment of risks and vulnerabilities of the banking sector. The EBA collects reporting data from close to 200 banks in the European Union, regularly evaluates the risks inherent in the sector and conducts stress tests every two years. The next round will be held in the next year.
How does the EBA see its strategic challenges for the next four years?
In addition to the development of the Single Rulebook, it will expand the monitoring of consistent implementation of the rules contained therein to subsequent areas. At the same time, shortly after the introduction of the prudential rules from the CRD IV/CRR package, it was observed that the directive was insufficiently subordinated to one of the main principles of European law ‒ the principle of proportionality. An open discussion is now beginning on the strengthening of this principle and ensuring that small banks and those with simple business models – such as, for example, cooperative banks ‒ can enjoy less strict requirements than those applying to large institutions.
Over the next years the supervision authority will exert pressure on banks – also when it comes to substantive solutions and recommendations – to actively manage NPLs and restore lending to the economy. Another strategic area is the adjustment of the banks’ structure of liabilities to the requirements of the BRR directive, providing for their resolution, and the standardization of eligible liabilities which could be converted into equity capital and allocated for covering losses in the event of bankruptcy (MREL). The recommendations of the EBA will also relate to effective and coordinated crisis management in the European Union as a whole, reporting of financial institutions, as well as, among others, corporate governance.
The EBA will also have to face the challenges brought by financial and technological innovation. They will change the business models of banks, but also open up new areas for activity in the field of consumer protection. The EBA also intends to analyze the risks resulting from the weaknesses of the banking sector for individual states and other sectors.
Each of the listed seven strategic areas is divided into a set of activities that are described in detail. In total there are 38 activities envisaged in the program. Apart from them, in 2017 the EBA expects new challenges arising from the next batch of regulations announced by the European Commission, which aim at completing the construction of the banking union. These include, among others, a review of the CRR and the introduction of the rules of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) concerning the banks’ trading book, the implementation of the total loss absorbing capacity (TLAC) for the largest banks in the world, and the rules of safe securitization.
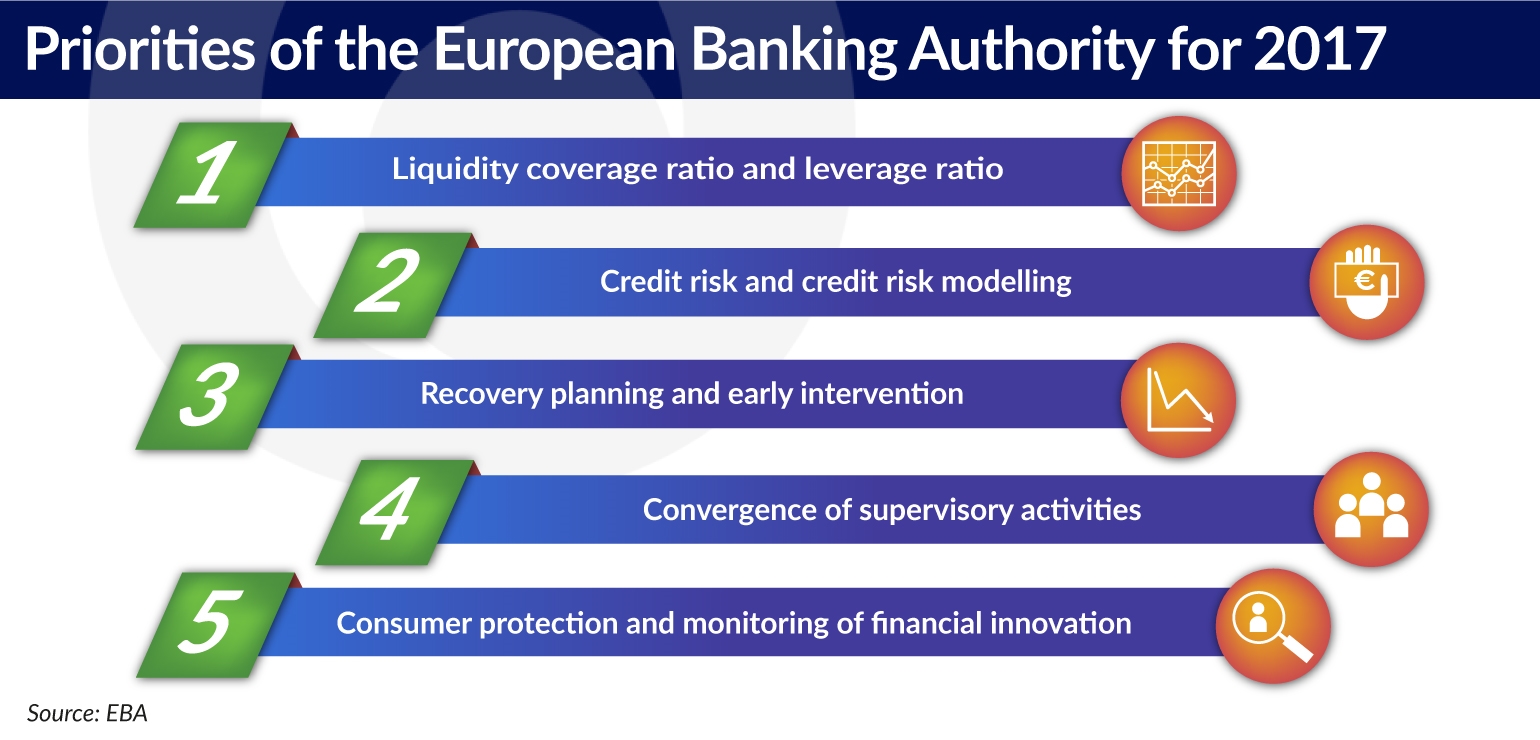
The most important elements in the 2017 EBA work program are:
- the technical standards for the leverage ratio and supervisory reporting, as well as measures allowing for the monitoring of short-term liquidity coverage ratio;
- the assessment of the adequacy of the banks’ internal models used to analyze the credit risk, i.e. the IRB approaches;
- the technical standards and guidelines for the establishment of recovery planning and early supervisory intervention envisaged by the BRR directive;
- the promotion of convergence in supervisory activities, especially in relation to the recommendations of supervisory bodies concerning Pillar 2 and the evaluation of banks’ internal models;
- the improvement of consumer protection rules, the monitoring of financial innovation and the technical standards for the PSD2.
The European Banking Authority was established in 2010, along with several other EU agencies, with the goal of creating a safety network for the European banking sector.