The ECB seems to think that cheap multi-year loans will get the European banks to resume their lending to small and medium businesses and households. However, European banks remain saddled with bad loans. European financial firms are trying to sell portfolios of soured loans and distressed assets. Dollar-based investors are reportedly featured buyers. The capital inflows coupled with the large current account surplus bolsters the euro.
European officials, like US officials, initially wanted to figure out schemes to remove the „toxic” assets from financial institutions. For various reasons, this did not work out, generally, though there are bad banks that have warehoused, packaged and sold some of the troubled loans.
The LTROS essentially gave banks the means to boost profits (carry trade) so that they can service their bad loans easier. The TLTROS are meant to give banks access to cheap capital to lend out.
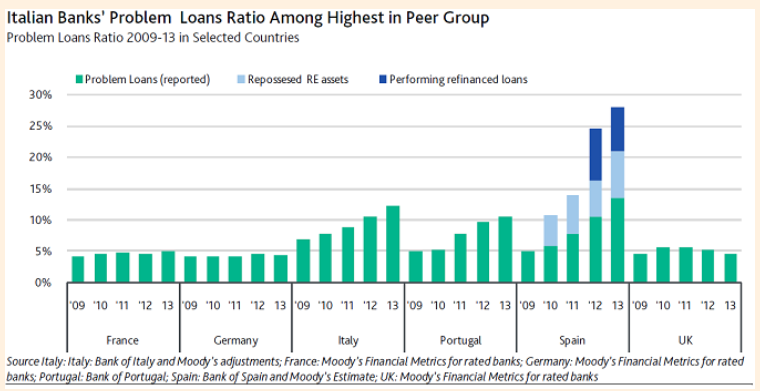
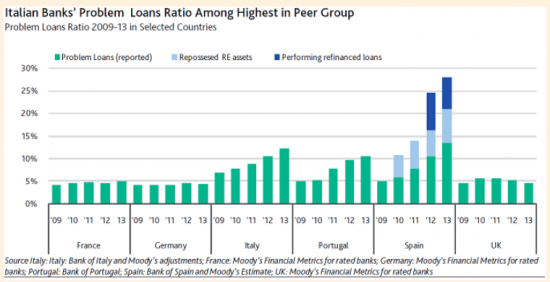
This Great Graphic was posted by the Financial Times, but comes from Moody’s. It shows the problem loans (green bar) for a selection of European countries. Spain and Italy stand out. Italian banks have the most bad loans in Europe, even though the hangover from Spain’s housing market bubble leaves it with serious challenges. Moody’s has reiterated the negative outlook for Italy’s financial sector. Last year, Italian banks lost a combined 20.6 bln euros. Moody’s expects core revenues to be only slightly higher this year.