German automotive industry at a crossroads
Kategoria: Business
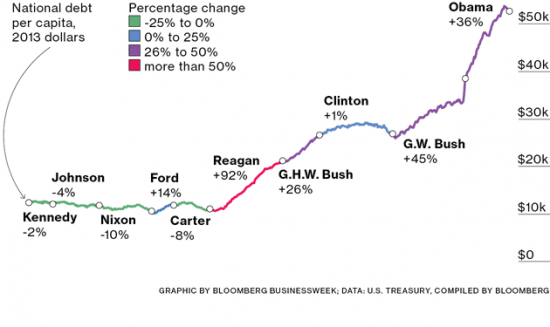
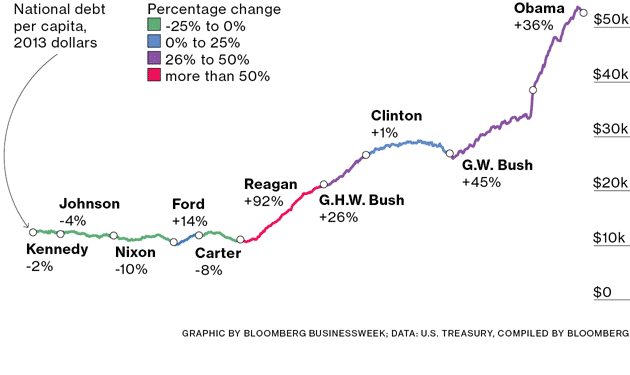
This Great Graphic will likely surprise many. Work by Giovanni Salzano at Bloomberg Businessweek, drew on US Treasury data to show the changes in the debt per capita under different presidential administrations, since 1960. The data is adjusted for inflation and displayed in 2013 dollars.
Before Obama’s second term is up, debt per capita is likely to have grown as much as it did under G.W. Bush, which is not quite twice what it grew under G.H.W. Bush’s single term. However, it is Reagan to whom the dubious honor goes for presiding over the nearly doubling of the US debt per capita.
Ford, who finished Nixon’s second term, deserves special mention. His short tenure produced the first increase in US debt since Truman and largely unwound the reduction in debt that occurred under the Nixon’s six years in the White House. Clinton’s two terms stand out, but in the opposite direction. On his watch, the American debt per capita rose 1%.